
Recycle House Waste for Clean Environment
IDEATHON 2023: Strategic Intervention for Developing Sustainable Entrepreneurial Ecosystem in Jharkhand
By: Er. S.P. Sharma, B.E. (IITR), MBA
Dr. S. K. Das
Problem Statement and Executive Summary
Environmental pollution has reached a critical level, especially in big cities, making it challenging to live healthily. Many cities in India rank among the world’s most polluted, with Delhi NCR often experiencing air quality index (AQI) levels reaching as high as 500. Traditional governmental measures, such as vehicle restrictions and construction bans, have had limited success in improving air quality. This project proposes recycling household waste as a sustainable solution to mitigate pollution and reduce individual expenses.
Social Problem
Maintaining a clean environment is a collective responsibility. Government efforts like vehicle restrictions and bans on diesel and petrol vehicles have not significantly improved air quality. The AQI levels in Delhi NCR often remain in the severe category, necessitating innovative solutions.
Objective of Business Plan
The goal is to recycle household waste into useful products. The project focuses on five types of household waste, utilizing patented technologies:
- Kitchen Solid Waste through Biorefinery
- Toilet Liquid Waste
- Kitchen Biodegradable Waste through Biogas System
- Use of Cow Dung in House Building
- Recycling Flowers and Leaves from Puja Rooms
Technical Executive Plan
- Kitchen Solid Waste Biorefinery Processing:
This process extracts nutrients from kitchen solid waste using patented technology, creating products beneficial for organic agriculture, aquaculture, and animal health. These products are cost-effective, eco-friendly, and have shown positive results in farming practices.
- Toilet Waste Recycling Systems:
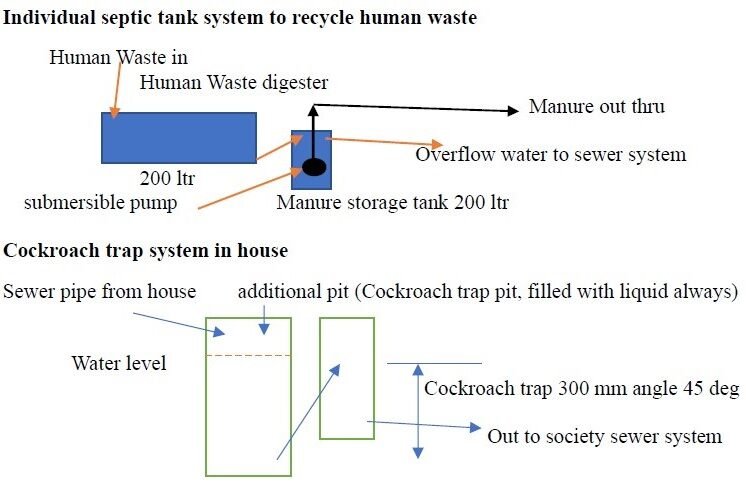
Transforming toilet waste into odor-free manure for home vegetable gardening. This system can reduce sewer waste by 50% and simultaneously provide fresh vegetables. Additionally, it includes a cockroach trap to prevent infestations from sewer systems.
- Home/Family Biogas System:
A biogas system to convert food waste into biogas for cooking and manure for gardening. A household producing 5 kg of waste per day can generate 30 minutes of stove biogas daily.
- Use of Cow Dung in House Building:
Utilizing cow dung to produce gobar paint, plaster, lakdi (sticks), and bricks. These materials are environmentally friendly and can replace traditional building materials, offering better thermal regulation in homes.
- Recycling Flowers and Leaves from Puja Rooms:
Collecting and drying temple flowers and leaves to produce scented sticks and dhoop, using essential oils and cow dung/urine.
Financial Viability Plan
The projects are self-sustainable, converting waste into marketable products that improve the environment and generate income.
Marketing Plan
Skilled manpower will be utilized to implement projects across various locations, supplying local markets and users.
Timeline of Execution
The transition from concept to working model can be achieved within three months.
Conclusion
These innovations, developed by retired scientists and professionals, aim to create livelihood opportunities for unemployed youth and women. Establishing training centers can help unemployed individuals adopt these new employment opportunities. Government incentives for recycling industries can further enhance the viability and adoption of these systems, leading to cleaner cities and improved public health.
Through these initiatives, the project seeks to empower communities, promote environmental sustainability, a
